low end tidal co2 during cpr
Why is ETCO2 low during CPR. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
End tidal carbon dioxide is not a good predictor of compression depth or blood flow during CPR.

. Low ETCO2 below 10 mm HG may be caused by either poor compression technique or from low perfusion and metabolism after a long downtime or shock despite good. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. Low ETCO2 below 10 mm HG may be caused by either poor compression technique or from low perfusion and metabolism after a long.
Carbon Dioxide During the Low Flow State Initiation of CPR During CPR chest compressions along with positive pressure ventilation restore organ perfusion and oxygenation to some. The dynamic pattern of PetCO2 values during out-of-hospital CPR showed higher values of PetCO2 in the first two minutes of CPR in asphyxia and a prognostic value of initial. It has been suggested in several studies that a decline in ETCO2 is an indicative of the need to swap the personnel providing compressions during CPR.
The aim of this study was to compare patients treated with the mechanical chest compression device Autopulse with patients treated with conventional CPR. The respiratory tidal volume is composed of alveolar gas volume and dead space. 96 Suppl169 Morgan RW.
End-tidal CO 2 monitoring during CPR is a relatively new area in which research is ongoing. What is end tidal CO2 and why is it important during a Code Blue. The coronary perfusion pressures during the first breaths of CPR did not differ between the two groups.
Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient perfusion which. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. During CPR the blood flow to the lung may be so low that few alveoli are perfused.
End tidal carbon dioxide CO2 correlates with cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients. High CO2 levels are indicated by low. Approximately one third of the tidal volume in healthy patients is dead space see Fig.
This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement. Increasing CO2 during CPR can also. Likewise the Return of Spontaneous.
On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing airway obstruction or respiratory distress. Conversely several studies have demonstrated that low etCO 2 during CPR indicates low probability of survival. High initial PetCO2 did not correlate with return of spontaneous circulation.
End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled. Of CO2 is inversely indicated by the amount of light that passes through the sensor. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring during.
Ensure proper rate approximately. 96 Suppl169 Resuscitation 2015. End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status.

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationwhen Is Capnography Useful In The Ed Part Ii Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
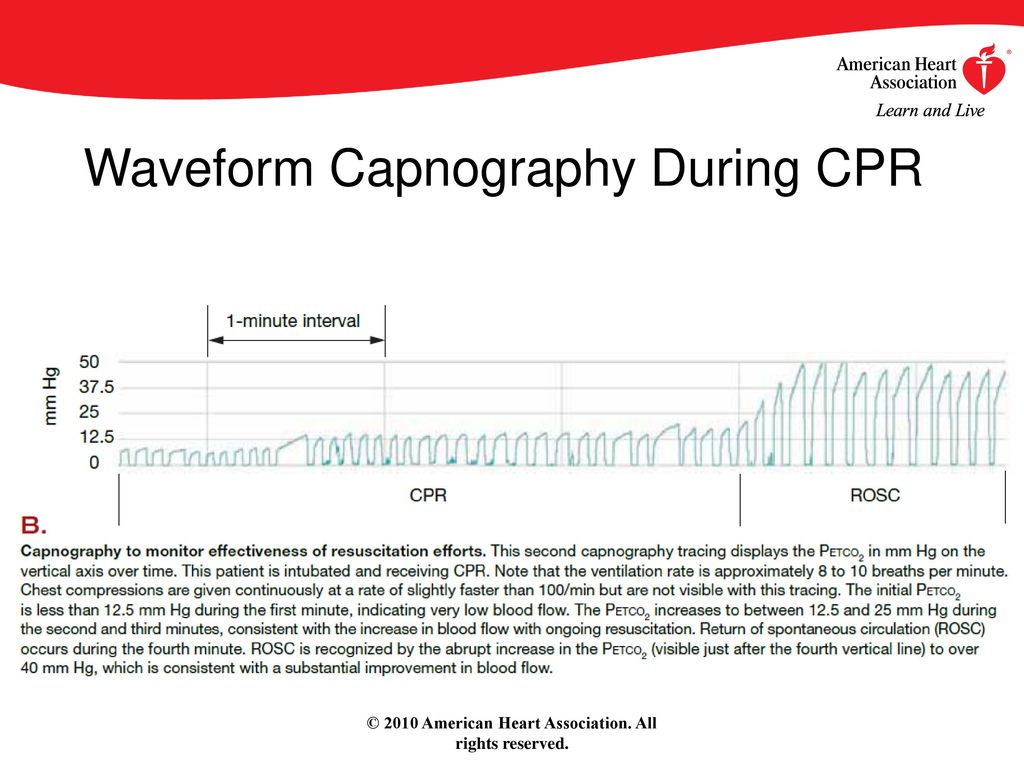
New Adult Cardiovascular Life Support Guidelines Ppt Download

Rogue Capno Waves Resuscitation Team Notes Unusual Waveform During Cpr Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

End Tidal Co2 In Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Etco2 In Cpr

Initial End Tidal Co2 Partial Pressure Predicts Outcomes Of In Hospital Cardiac Arrest The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine
How To Use End Tidal Capnography To Monitor Asthmatic Patients Acep Now

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Umem Educational Pearls University Of Maryland School Of Medicine Department Of Emergency Medicine

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
End Tidal Co2 The Drummer Of The Vital Sign Band Pem4

End Tidal Co2 Monitoring Noninvasive Respiratory Monitoring For The